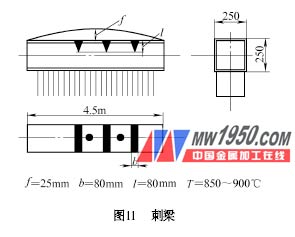
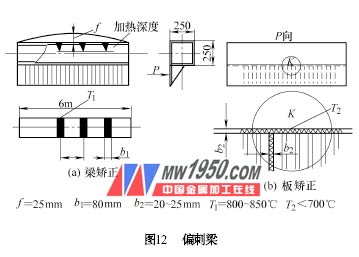
The second lecture is the correction of the deformation of the column workpiece (top) 1. The correcting thorn beam for the deformation of the thorn beam is a member mainly composed of double splicing steel (see Figure 10). Due to the dense welding of the δ=10mm steel plate on one side, severe deformation is inevitable. Correction first uses the belt to heat the arch surface. If it is not completely straight after correction, it will be supplemented by the method of dot heating. The box-shaped main body of the thorn beam (see Figure 11) is corrected by the combination of two sides of the triangle and the arched surface with the heating zone. The heating sequence starts from the tip of the triangle, and the triangle is followed by the line, which is in the channel and the coincident part. Extend the heating time to make the heating zone red. 2. Correction of deformation of the slanted beam The slanted beam is an up-and-down and left-right asymmetric structure (see Figure 12), which must be deformed in two directions during welding. Correction is divided into main beam correction (see Figure 12a) and correction of one side of the steel plate (see Figure 12b). For the correction of Figure 12b, the heating must be controlled below the specification. If the temperature is too high, redness will occur and there will be no correction. If it is not completely straight after one heating, it needs to be supplemented after the workpiece is cooled. The supplementary heating wire should leave the original heating wire. 3. Correction of small column deformation (2) The double-stacked column of double-stacked column deformation (see Figure 14) is a workpiece that is fastened by two channel steels. Its rigidity is poor. It is not suitable to use a large heating zone, otherwise it will produce reverse deformation, or no Corrective effect. The deformation of f 1 is due to the deformation caused by the welding of the one-sided bracket, and the heating form of the dot is employed. The dots are baked on the center line of the workpiece, one heating point on each side of the bracket; the deformation of f 2 is caused by the double-welding of the profile steel, the corrected dot is smaller than the dot of f 1 , and the dot is baked on the large surface of the channel The heating area and temperature should be the same on the same horizontal line on both sides. (3) The deformation of the small box-shaped column is corrected by a combination of a triangle and a belt. For the deformation of the bracket portion, the correcting method is shown in Fig. 15. The heating zone is baked on both sides of the bracket with the bracket position instead of facing the bracket to improve the correcting ability. The triangle of the heating zone is baked on both sides of the column, and the position is symmetrical, and the area and temperature are uniform. B2 in Fig. 15 is a supplementary heating zone. After the correction heating is completed and cooled, the b2 heating line width is selected depending on the amount of deformation of the workpiece. Previous Next 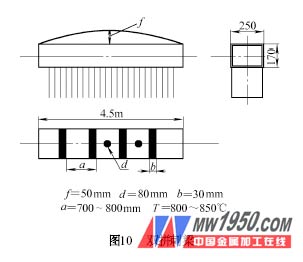
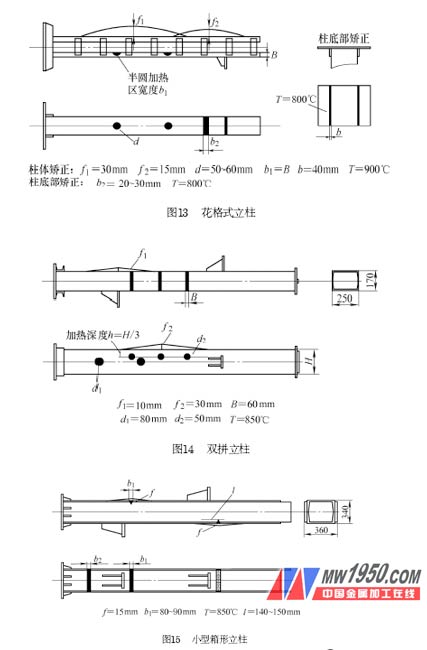
There are many types of small columns. In this paper, the flower format column, double-stack column and box-shaped column are typical examples, and the correction method of deformation is introduced.
(1) The corrective specification of the correct flower pattern column for flower format column deformation is shown in Figure 13. If the correction of f 1 is not completely straight, after the workpiece is cooled, supplemental heating is performed on the edge of the original heating wire, and the width of the supplementary heating wire is slightly smaller than the original heating wire. The small semi-circular heating point corrected for f 2 is baked on the small surface of the channel and required to be symmetrical up and down to prevent other deformation.