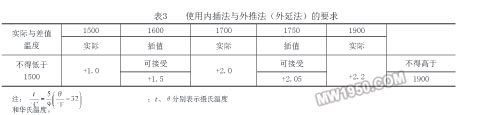
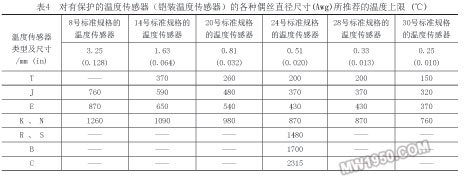
The correction factor between the two known points of the temperature sensor (when the correction coefficients of the two temperature detection temperature points are known) (calculating the correction factor of a certain temperature between the two temperature detection temperature points) is allowed to be used within The interpolation is obtained, and the correction coefficients outside the two known points are not allowed to be obtained by extrapolation (epitaxial method) (see Table 3 for details). Interpolation: is the correction factor between two known points of the temperature sensor (when the correction coefficients of the two temperature detection temperature points are known) (calculating a temperature between two temperature detection temperature points) The method of correcting the coefficient). Interpolation can use a precise ratio value (interpolation) for a linearly good temperature sensor to obtain a corresponding correction factor; for a less linear temperature sensor (especially for a cheap metal temperature sensor like a K-type temperature sensor) ) The cage should be caged out with the correction factor and the temperature curve, and the correction factor should be read from the corresponding curve. The interpolation method is applied to the following two cases: In the first case, it is assumed that there is a straight line distribution between the check points (the correction coefficient varies linearly with temperature); the second case is not always like the first case. That way, especially for inexpensive metal temperature sensors like K-type temperature sensors. Selection and use of temperature sensor correction factor: First, assume that the correction factor is the highest, lowest or closest correction factor of 140 ° C (maximum calibration range); second, the method used must be consistent; third, the internal program file must A clear explanation of the method of selecting the correction factor. Sixth, AMS2750D "High Temperature Measurement" specification for the use of temperature sensors and requirements 1. Regulations and requirements Temperature sensor usage requirements are as follows: Temperature sensor can only be used in ASTM MNL 12 Table 3.1 [Recommended temperature limits for protected temperature sensors (armored temperature sensors)], ASTM MNL 12 Table 3.5 [For protected temperature sensors ( Recommended temperature limit for armored temperature sensor], ASTM E 230 Table 6 [Recommended upper temperature limit for protected temperature sensor (armored temperature sensor)] (see Table 4 for details), ASTM E 608 Table 1 [pair The temperature limit recommended by the protected temperature sensor (armored temperature sensor) (see Table 5), as well as other national standards, temperature sensor suppliers listed in the temperature range. For the use of temperature sensors that do not meet the above recommendations and recommendations, they should be verified according to the requirements of the calibration interval in Table 1 of this specification. The temperature sensor calibration interval specified in this specification is the maximum allowed regardless of the time of use, the number of uses, or the temperature of use. According to the temperature sensor calibration interval specified in this specification, the user is not responsible for ensuring that the temperature sensor does not excessively drift under certain conditions of use (environment, time, temperature). That is to say, even if the temperature sensor calibration interval requirements specified in this specification are met, it is not certain that the temperature sensor will not excessively drift under certain use conditions (environment, time, temperature). Users should have system accuracy check, temperature uniformity test, and repeat check data, but should not be limited to these data support. The user should also have a written control program for the maximum life of the special case (life limit) and the maximum number of use of the temperature sensor replacement. Previous Next